
TRANSITIVE INTRANSITIVE VERBS IN ENGLISH ACTIVEPASSIVE VOICE PART3 YouTube
1. The bystanders laughed. 2. The watchdogs bark. 3. Snow is falling. An intransitive verb followed by a preposition is often used in the passive, the object of the preposition becoming the subject of the verb. Active Voice…….Passive Voice 1. Everybody laughed at him..…. He was laughed at by everybody. 2.

73 Intransitive Verb Examples List English Vocabs
An intransitive verb is a "verb that indicates a complete action without being accompanied by a direct object, as sit or lie, and, in English, that does not form a passive." Our definition does a good job of saying what an intransitive verb is, but let's break the two major points a little more. 1.

Intransitive verb, Verb, Transitive verb
Lesson 118 Parts of the Sentence - Transitive and Intransitive Verbs. Transitive verbs are verbs that have subjects or objects that receive the action. They are either active voice or passive voice.. Transitive active verbs are the verbs in sentences with a direct object. The subject The subject tells who or what about the verb.Source: Lesson 91 is the doer and the direct object A direct.

80 Learn Japanese 【Passive Sentence of Intransitive Verbs】 受動態 YouTube
What is a transitive verb? You can categorize all verbs into two types: transitive and intransitive verbs. Transitive verbs use a direct object, which is a noun that receives the action of the verb.Intransitive verbs do not use any objects. Let's look at an example with one of the most common transitive verbs, need. We need a bigger boat.; Here, the transitive verb need takes the direct.

PPT THE PASSIVE PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID5386184
The Collins Dictionary defines a transitive verb as "a verb accompanied by a direct object and from which a passive can be formed, as 'deny', 'rectify', 'elect'". The Merriam-Webster Dictionary gives a similar definition. According to them, a transitive verb is "characterised by having or containing a direct object". What Is an Intransitive Verb?
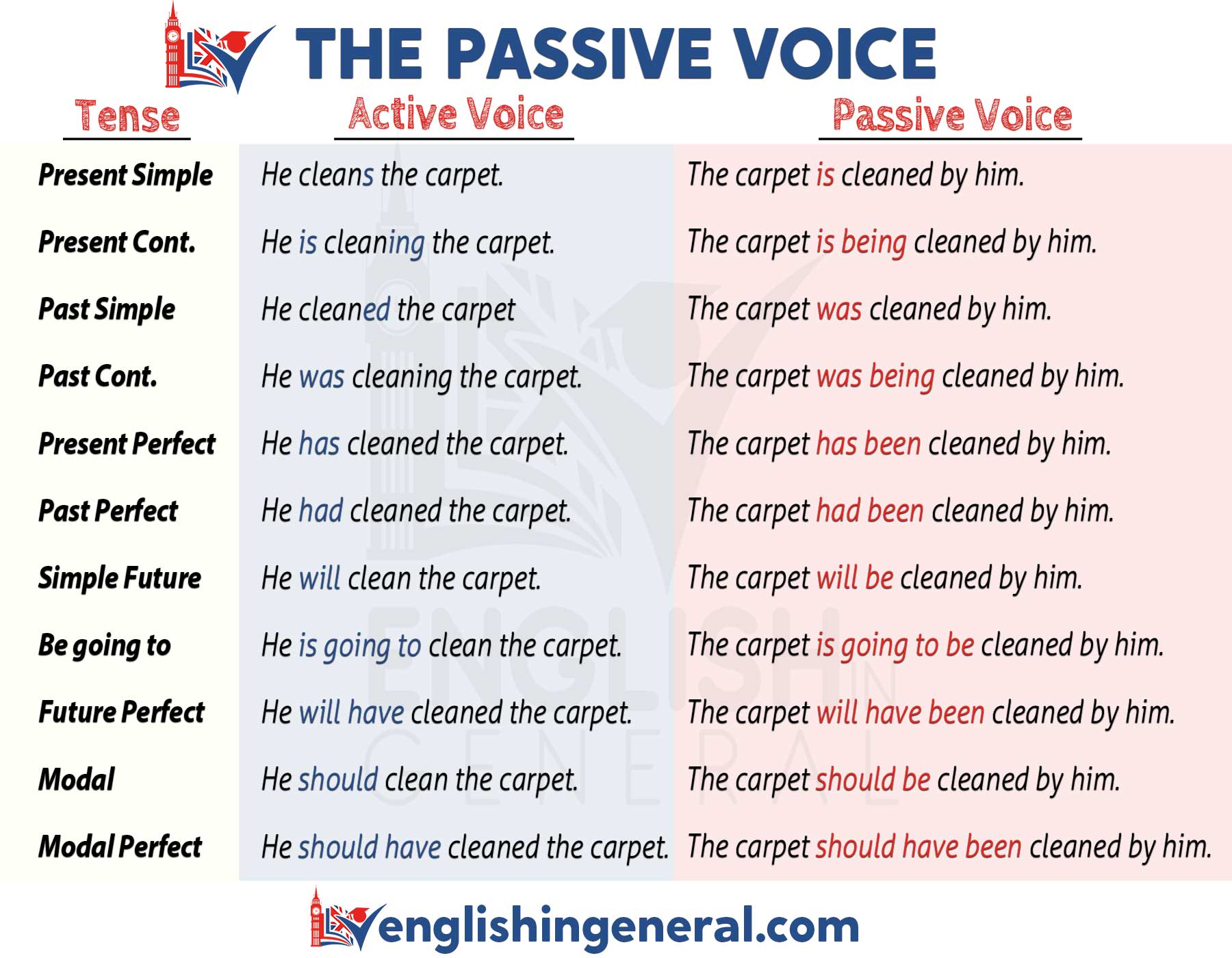
The Passive Voice Grammar Lessons English in General
A transitive verb is a verb that requires an object to receive the action. Example: Correct: The speaker discussed different marketing strategies in the video. Incorrect: The speaker discussed in the video. The verb "discuss" requires an object ("different marketing strategies"). It is necessary to state what the speaker discussed.

Passive Voice Sukrisno Nino
Intransitive verbs, or verbs that cannot take a direct object, cannot be passive. You cannot say "I was arrived by train" because the intransitive verb arrive cannot be followed by an.

PDF active and passive voice exercises with answers pdf PDF Télécharger Download
Intransitive verbs. Intransitive verbs (verbs that do not take an object) cannot be passive. For this reason, the following sentences have no passive equivalents: We arrived home late at night. Did you sleep well? He was running too fast. Certain state verbs. Certain state verbs are not used in the passive even if they are transitive.

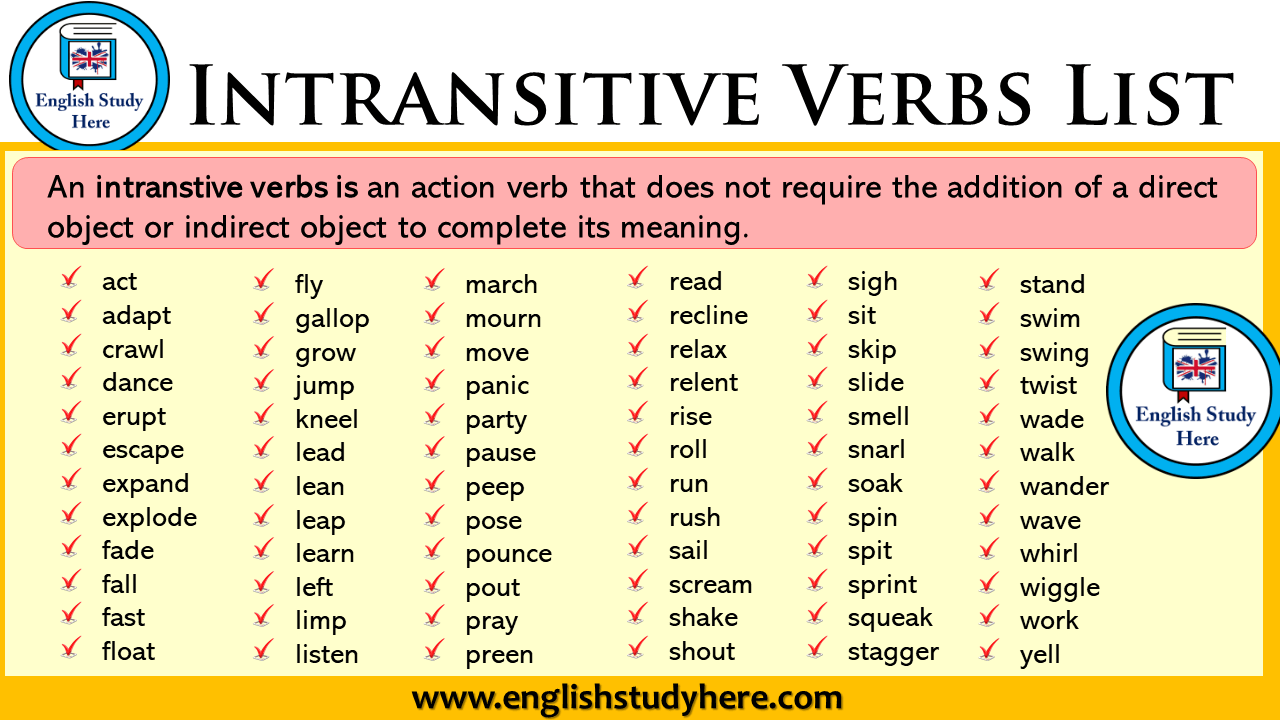
Intransitive Verbs English Study Here
The change from passive to active voice works like this: subject verb object - active voice. object verb - passive voice. An intransitive verb, by definition, does not have an object, so you cannot form a passive voice version from an intransitive verb. Many verbs can be used both transitively or intransitively: sometimes the meaning is different.
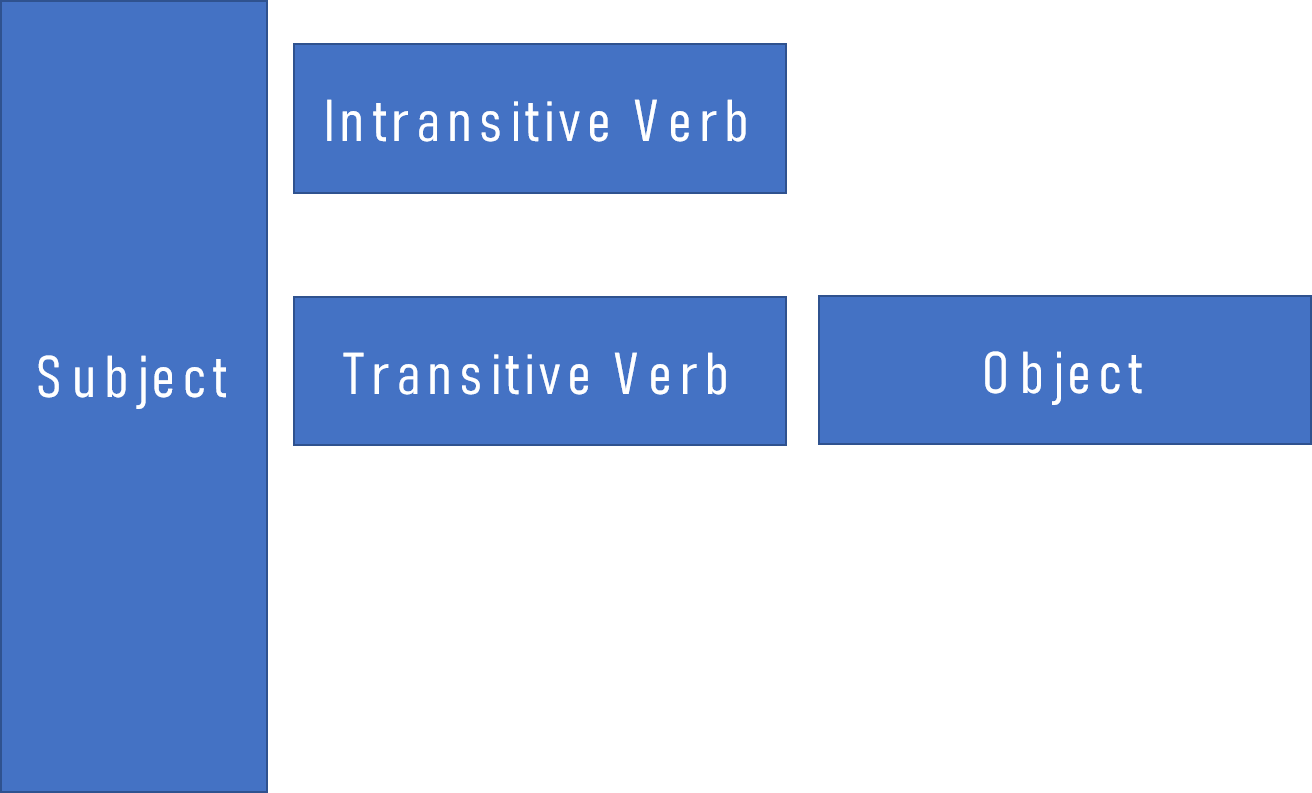
Transitive & Intransitive Verbs Red & White Matter Classes
If it can take an object, it can be used as a transitive verb. Intransitive Verbs An intransitive verb is a verb that cannot have an object. For example, the verb sleep. People sleep. ( subject )+ ( verb ). In this example, there is only a subject (the person doing the action) and a verb. There is no object.
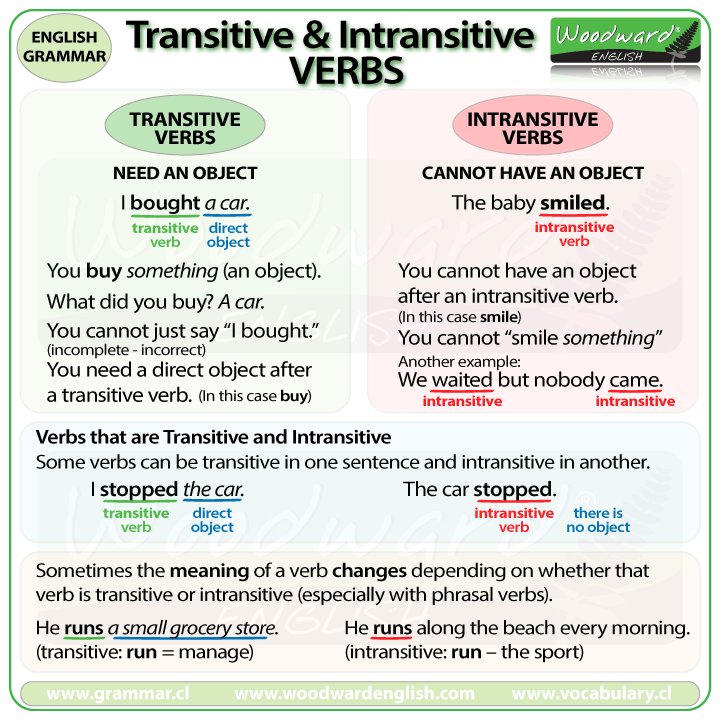
Transitive and Intransitive Verbs Effortless English
("Ate" is a transitive verb. The action of the verb was done to something ("an apple"), which is the direct object.) Show me an infographic Table of Contents What Does "Taking a Direct Object" Mean? Examples of Intransitive Verbs Verbs That Are Transitive and Intransitive Common Intransitive Verbs Intransitive Verbs Do Not Have a Passive Form
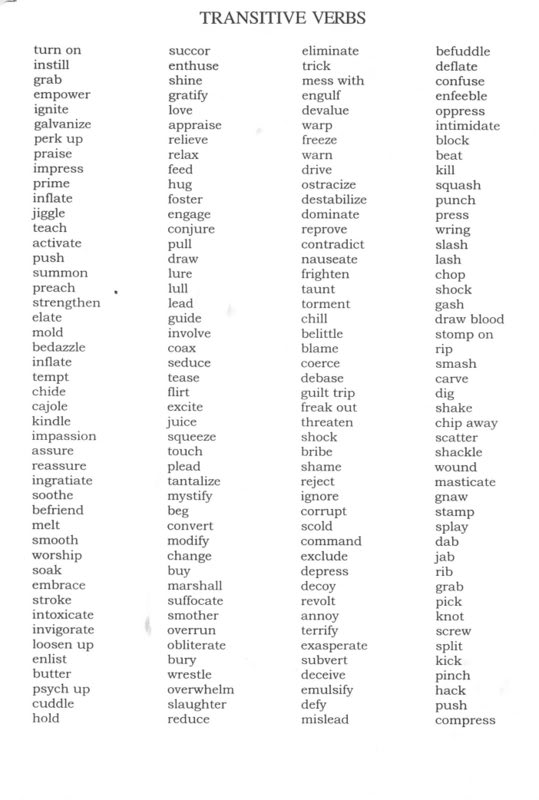
TRANSITIVEINTRANSITIVE VERBS IN PASSIVE aslıhan's websıte
The verb in the transitive passive voice always has is, am, are, was, were, be, being, or been as an auxiliary or helping verb. Transitive active sentences can be changed to transitive passive sentences by making the direct object the subject and putting the subject either in a prepositional phrase or omitting it.

Passive Voice Transitive & Intransitive Verbs
An intransitive verb is a verb that doesn't require a direct object (i.e., a noun, pronoun or noun phrase) to indicate the person or thing acted upon. For example, the verb "yawn" is intransitive because it's not possible to "yawn" something. The opposite is a transitive verb, which must take a direct object.

Intransitive Verbs The Grammar Rule You're Probably Breaking Without Even Knowing It ESLBUZZ
Revised on March 14, 2023. A transitive verb is a verb that requires a direct object (e.g., a noun, pronoun, or noun phrase) to indicate the person or thing acted upon by the verb. For example, in the sentence "I received a letter ," the direct object is necessary for the statement to make sense. In contrast, an intransitive verb is a verb.
Intransitive Verbs List in English English Study Here
A verb can be described as transitive or intransitive based on whether or not it requires an object to express a complete thought. A transitive verb is one that makes sense only if it exerts its action on an object. An intransitive verb will make sense without an object. Some verbs can be used both ways. How to identify a transitive verb
I understand that the prefix di is used to form passive transitive verbs, while ter is used to
The words "listen", "laugh", "work" and "look" etc. are intransitive verbs, but why are they used in passive sentences with preposition "to", "at" and "on" etc.? He laughed at me [I was laughed at by him] I worked on the computer [The computer was worked on by me] I listened to him [He was listened to by me] I looked at him [He was looked at by me]